Global trade is changing at a breakneck pace, supported by technology that continues to open up new possibilities never seen before.
Smart factories, the Internet of Things, robotics, location technologies, advanced human-machine interfaces, 3D printing, augmented reality, big data and 3D technology, among other examples, are redefining the way companies produce and whose customers research and interact with the products before buying them.
Industry 4.0 is a new wave that will redefine commerce for decades to come. However, in order to fully grasp the nature of openness change in Industry 4.0, it is necessary to understand what the first three industrial revolutions were.
Industry 1.0 and 3.0
The first industrial revolution (Industry 1.0) took place between 1760 and 1840. This period was marked by a shift from manual production to manufacturing using machines mainly powered by steam and water. Many industries are affected by this change, including the iron industry, agriculture and mining.
The second revolution (Industry 2.0) happened between 1870 and 1914. It is better known as the technological revolution. At that time, technological progress allowed a considerable improvement in the means of communication and transport.
The second revolution (Industry 2.0) happened between 1870 and 1914. It is better known as the technological revolution. At that time, technological progress allowed a considerable improvement in the means of communication and transport.
The third revolution takes place in the second half of the 20th century. This is called the digital revolution. The influence of computers has become prevalent in almost every sector of industry and in every aspect of society. Communication is further improving with the advent of tools such as the Internet and email.
What is Industry 4.0?
The fourth industrial revolution is marked by the digitization of production and the computerization of industry, it is a new wave that will redefine commerce in the decades to come.
Industry 4.0 or the industry of the future corresponds to a new way of organizing the means of production. The expansion of 4.0 is the desire of companies to digitize their processes. More and more companies want to digitize and automate their activities, with the aim of increasing productivity, profits and their competitiveness.
Industry 4.0 applies mainly to smart factories that integrate these technologies in order to automate as much as possible the production, packaging, transport of goods.
The goal of Industry 4.0 is:
- to make companies less dependent on the human labor force,
- increase their profit margins,
- dramatically increase production
- to automate the maximum of facets of the companies,
- adapt more easily to changing customer needs
- to eventually develop machines that adapt and learn on their own.
- The smart factory: safe, connected and flexible production
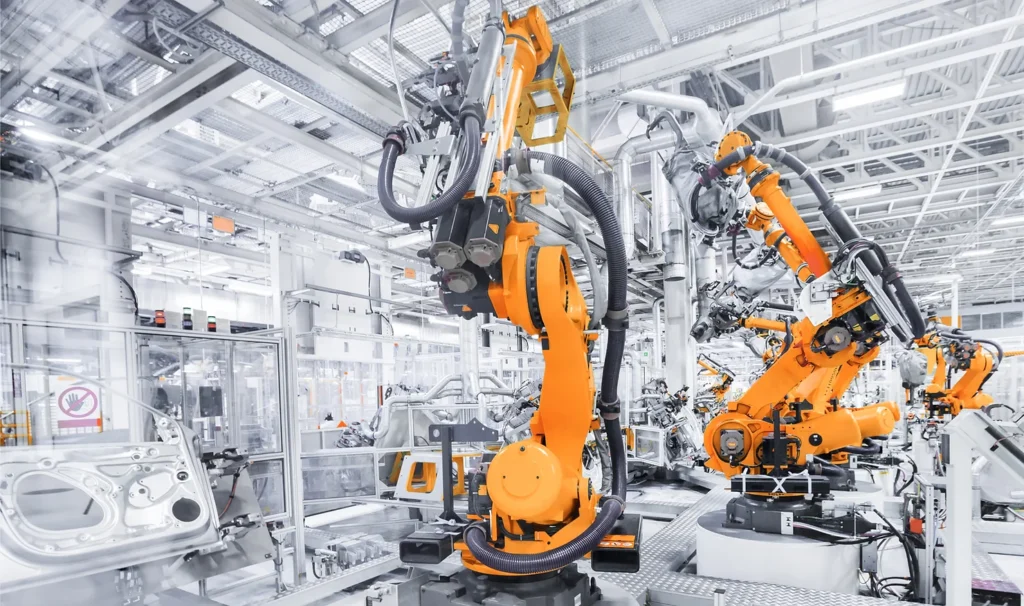
Smart factories are a key part of Industry 4.0. They are designed to be highly efficient, secure and cost effective, using advanced robotics, big data processing, cloud computing, enhanced cybersecurity, smart sensors and other advanced features.
With this approach, companies can optimize their production to accommodate mass customization, while securing their premises, making them less dependent on human labor and therefore more profitable.
In smart factories, robots do the majority of the work needed to manufacture products. Most of the machines used in smart factories are powered by artificial intelligence and can perform high-level tasks. In some cases, they can even make decisions and learn from their experience.
In addition, since the majority of smart factories are equipped with sensors, the machines can notify their operators of an impending breakdown or any malfunction.
With this advance information, mechanics, engineers and operators are able to repair and/or replace faulty machines before they cause more serious problems. It is estimated that smart sensors can help businesses reduce downtime and save up to 40% on maintenance costs.
Smart factories offer so many benefits to businesses that they are enjoying increasing popularity. More and more companies are turning to this type of plant.
It is even estimated that smart factories will generate more than $500 billion in value by 2022. The craze for smart factories is so great that about 76% of manufacturers are transitioning or planning to transition. It is also estimated that smart factories will increase their productivity sevenfold by 2022.
The advent of new technologies: automation, customization, 3D printing, artificial intelligence.
Comme toutes les révolutions industrielles qui la précèdent, la révolution de l’Industrie 4.0 augmentera considérablement notre capacité à fabriquer des produits, à les expédier dans le monde entier et à améliorer l’expérience client. Mais contrairement à ces autres révolutions, l’Industrie 4.0 permettra un développement sans précédent en matière d’automatisation, de personnalisation, de productivité et d’efficacité.
In addition, the large number of innovations underway worldwide should allow considerable progress to be made rapidly, particularly in the fields of biotechnology, energy storage, 3D technology and autonomous vehicles.
In the years to come, many people will drive autonomous vehicles, synthetic biology will revolutionize medicine, space exploration and travel will improve and expand, 3D printing will change the way we have and produce objects, as well as many other positive developments.
Through mass customization, smart factories and 3D configuration technology, companies will not only be able to increase their profit margins, but also improve the lives of their consumers by providing a better customer experience.
Conclusion: Industry 4.0, challenges and opportunities
One of the biggest challenges that Industry 4.0 will face is labor market disruption caused by automation, advanced robotics and AI. Computers and machines will be able to perform increasingly complex tasks and therefore put millions of jobs at risk. An expert in the field of AI even estimated that AI could replace up to 40% of existing jobs in the next 15 years.
However, each new industrial revolution also creates countless jobs. In the case of Industry 4.0, new perspectives will open up in the fields of blockchain, cybersecurity, big data, 3D printing, biotechnology, nanotechnology, aerospace and many more. others. Industry 4.0 will therefore create a significant number of opportunities.
Industry 4.0 has the potential to radically improve the lives of millions of people: many aspects of industry and commerce, from factory job safety to the shopping experience, are set to improve .